Introduction

Autism meltdowns, often misunderstood as intentional acts of defiance, are involuntary responses to overwhelming sensory experiences or emotional stressors faced by individuals on the autism spectrum. Recognizing the signs and implementing effective strategies can be crucial in helping individuals navigate these challenging moments. In this comprehensive exploration, we will delve into various strategies to support autistic individuals during meltdowns, emphasizing self-regulation, escape plans, sensory items, meditation, and calming routines.
Understanding Autism Meltdowns
Autism meltdowns are unique to each individual, triggered by sensory overload, communication difficulties, or changes in routine. Recognizing and understanding these triggers is vital for developing personalized strategies to manage and prevent meltdowns. It is essential to approach meltdowns with empathy, acknowledging that they are not deliberate acts of defiance but rather involuntary responses to stressors.
Teaching Self-Regulation
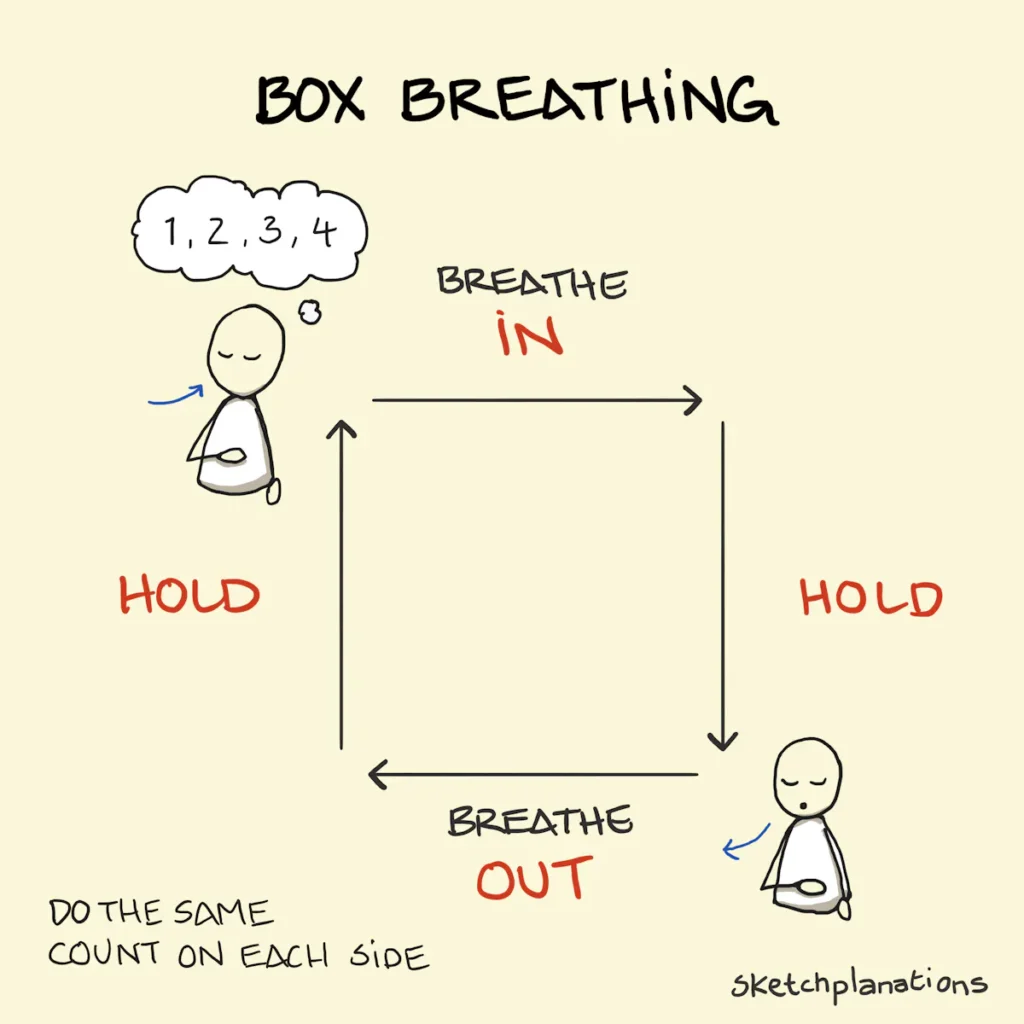
A fundamental aspect of managing autism meltdowns is empowering individuals with the tools to self-regulate. This involves helping them identify early signs of distress and providing coping mechanisms to regain control. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, visual aids, and self-soothing strategies can be incorporated into daily routines to foster emotional resilience.
Implementing deep breathing exercises allows individuals to regulate their physiological responses, reducing stress and anxiety. Visual aids, such as social stories or visual schedules, help in preparing individuals for changes or unexpected events, minimizing potential triggers. Additionally, introducing self-soothing strategies, like using stress balls or applying gentle pressure to specific sensory points, can assist in calming the nervous system.
Creating an Escape Plan
Developing an escape plan is crucial for preemptively addressing situations that may lead to meltdowns. Autistic individuals, along with their caregivers and support networks, can collaborate to identify safe and quiet spaces where they can retreat during overwhelming situations. Having a designated escape plan ensures that individuals can remove themselves from distressing environments, allowing for a more manageable emotional response.
An escape plan should be personalized to the individual’s preferences and needs. It may involve identifying safe spaces within familiar environments, such as home or school, where the individual can go to decompress. Communication is key in ensuring that caregivers and support networks are aware of the escape plan and can assist in its implementation when needed.
Utilizing Sensory Items

Sensory items play a pivotal role in helping individuals on the autism spectrum manage their sensory experiences. These items provide tangible and comforting ways to regulate sensory input, reducing the likelihood of meltdowns. Fidget toys, noise-canceling headphones, weighted blankets, or textured objects are among the tools that can be incorporated into an individual’s daily routine.
Fidget toys, such as stress balls or textured objects, provide a constructive outlet for excess energy and sensory stimulation. Noise-canceling headphones can be invaluable in minimizing auditory triggers, creating a quieter and more controlled environment. Weighted blankets offer deep pressure stimulation, promoting a sense of security and calmness. Experimenting with different sensory items allows for a personalized approach to managing sensory sensitivities.
Incorporating Meditation Techniques

Mindfulness and meditation techniques are valuable tools for promoting emotional well-being and self-regulation. While traditional meditation practices may need to be adapted to suit individual preferences, the benefits are considerable. Teaching autistic individuals simple meditation practices, such as focused breathing or guided imagery, can empower them to navigate overwhelming situations more effectively.
Mindfulness techniques encourage individuals to focus on the present moment, promoting a sense of calmness and reducing anxiety. Guided imagery, which involves imagining a peaceful and safe place, can serve as a mental escape during stressful situations. Consistent practice of these techniques can contribute to overall emotional resilience and stress reduction, making them effective tools in managing and preventing meltdowns.
Establishing Calming Routines
Establishing consistent calming routines can help create a sense of predictability and stability for individuals on the autism spectrum. These routines act as preventive measures against potential triggers for meltdowns by providing a structured and familiar environment. Calming routines can include activities that promote relaxation, such as reading, listening to calming music, or engaging in sensory-friendly activities.
Creating a visual schedule or checklist for daily routines can assist in providing clarity and predictability. Individuals may find comfort in knowing what to expect throughout the day, reducing anxiety and preventing potential meltdowns. It’s essential to involve the individual in the development of these routines, considering their preferences and sensory sensitivities to ensure effectiveness.
Conclusion
Autism meltdowns present unique challenges for both individuals on the autism spectrum and their support networks. By implementing strategies focused on self-regulation, escape planning, sensory items, meditation, and calming routines, we can create a supportive environment that fosters emotional well-being and reduces the frequency and intensity of meltdowns. Recognizing the unique needs of each individual and working collaboratively to develop personalized strategies empowers them to navigate the world with greater ease and resilience. Through empathy, understanding, and proactive measures, we can enhance the quality of life for individuals on the autism spectrum and create a more inclusive and supportive community.

